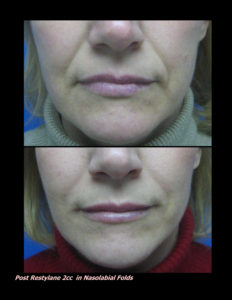
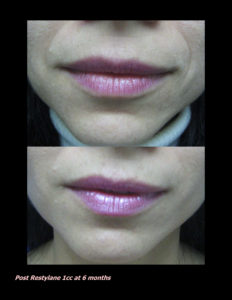
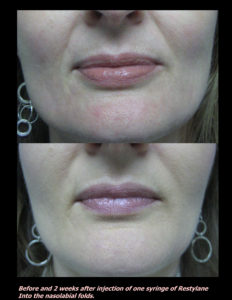
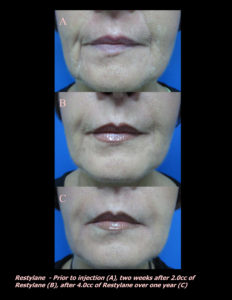
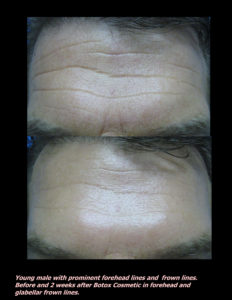
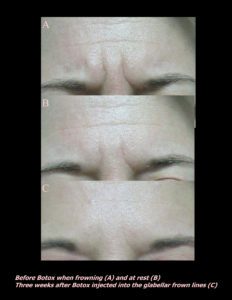
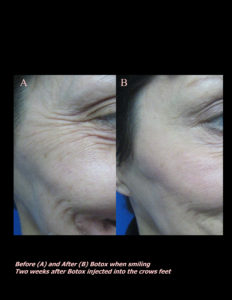
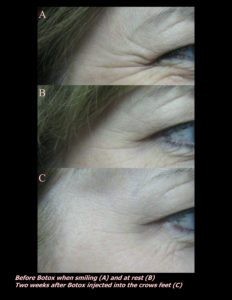
Red, white, and blue are not great colors for the skin
Raynaud’s phenomenon is a condition of the skin most commonly seen on the hands, feet, fingers and toes in up to 10% of Americans. In this condition there is an alteration of blood flow that can lead to altering appearing of red, white and blue as blood flow to the skin changes. Sometimes it is called Raynaud’s Disease or Primary Raynaud’s when no triggering disorder is identified and Raynaud’s phenomenon or Secondary Raynaud’s when it is part of an underlying disorder. We’ll just call it Raynaud’s.
Who Is Prone to Raynaud’s?
Raynaud’s phenomenon is most commonly seen in patients with connective tissue disorders, autoimmune diseases in the family of lupus. However, it can occur in patients without these disorders as well. It is usually seen in young women, but can be seen at any age and sex.
Why does the skin turn different colors?
White – Blood vessels shrink or close down limiting blood flow .
Blue – After extended periods of lack of blood flow bringing oxygen, the skin turns blue.
Red – The blood vessels relax and open again and the skin flushes with good blood flow.
Raynaud’s triggers
Most flares of Raynaud’s occur in cool or cold temperatures. Patients are often surprised when this occurs more in the Spring with donning flip-flops too early and in the fall when we are too slow at putting sandals away for the winter. Those who are prone to having Raynaud’s should attempt to avoid cold temperatures for their hands and feet. For some patients, Raynaud’s may be brought on by taking medications that cause constriction of the blood vessels such as OTC cold remedies. A less common form is seen in those who have a job where they handle something that vibrates such as a jackhammer. The condition also is worse in those who smoke because nicotine affects the blood vessels.
How Can Raynaud’s be Treated?
Other than keeping the hands and feet warm and avoiding triggers, there are other remedies. Oral medications such as calcium channel blockers can help alleviate the spasming of the blood vessels for some patients.
Are There Any Long-Term Problems with Raynaud’s?
Some patients with more advanced cases of Raynaud’s can get bumps on their skin that turn into ulcers that can become necrotic or gangrenous and form a hard black permanent scab. These areas are prone to infection.
How Is it Diagnosed?
If you think you have Raynaud’s take some pictures the next time you notice the red, white and blue changes. Then schedule an appointment with your primary doctor, dermatologist or rheumatologist to discuss it more. If you think someone you know has Raynaud’s please forward them this article. Have some cool pictures of Raynaud’s? Share them with us on social media with the tag #wvderm. Have some tips for keeping Raynaud’s in check? Share those with us too. We’d love to hear what you think!
If you know someone who may find this article helpful, please share it with them! Follow us on social media this week, and subscribe to our growing YouTube channel! If you would like to receive these posts in your email inbox, Subscribe to our Site.














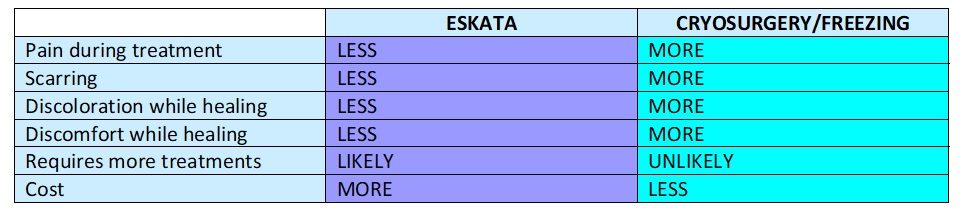
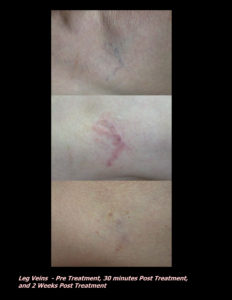
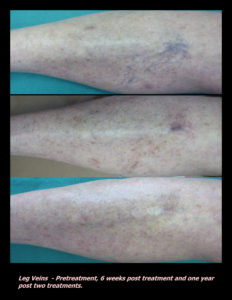
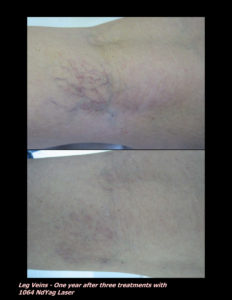
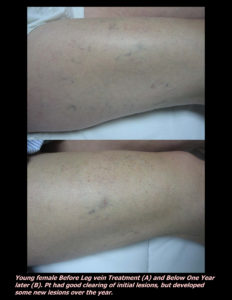
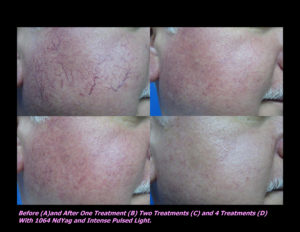
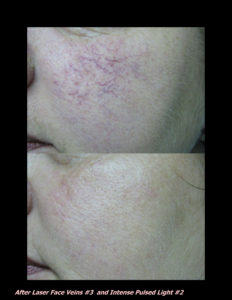
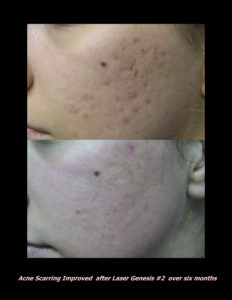
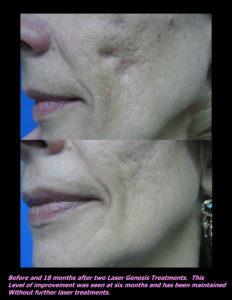
 Laser Vein Reduction Treatments
Laser Vein Reduction Treatments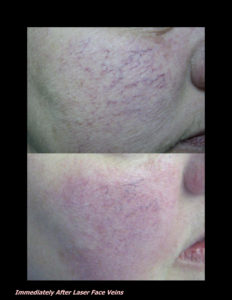
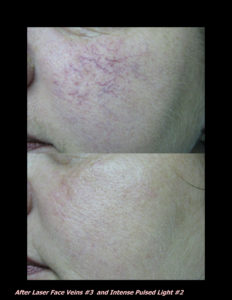



 DP Dermaceutical Products
DP Dermaceutical Products